Carbon Sliding Materials
About the product
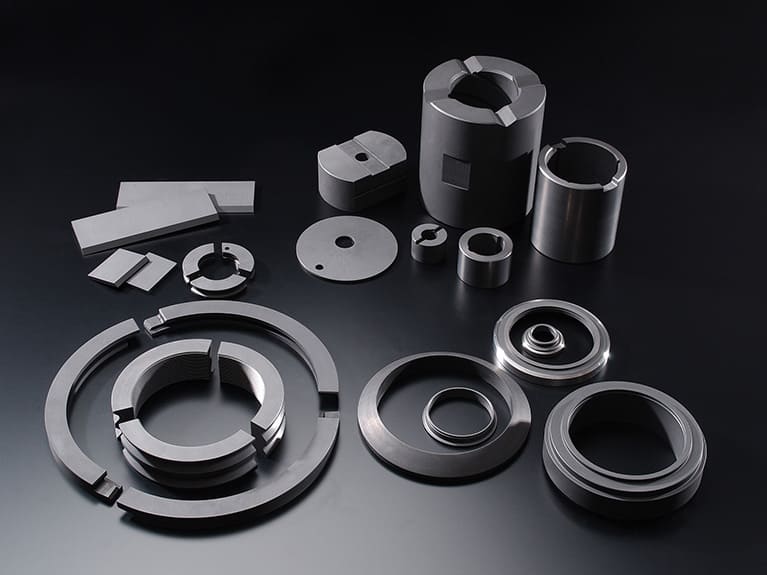

Carbon sliding materials have high self-lubricating qualities, and in addition, are excellent in thermal and chemical resistances. Such carbon materials have been used more widely as sliding material in many fields. Recently, they are used in paticular for anti-pollution purposes. Having started very early the development and manufacture of carbon materials in various many kinds, We are providing quality carbon products to meet the needs and demands from many different fields.
Features
| Item | Features |
|---|---|
| Chemical stability | The product has such a nature that it is not easily attacked by ordinary solution of acids, alkalis, of organic solvents.Chemical resistance is described in more detail in item 4 “Chemical properties”. |
| High thermal conductivity | Owing to its high thermal conductivity, heat generated at sliding part can be effectively dissipated. Thus, counterface material may not be damaged with minimized wear of the product. |
| High heat resistance | Heat can hardly degrade the machanical strength and chemical properties of the product. If ample oxygen exists, oxidation will be started at a temperature over 350ºC or so. When no oxygen is supplied, however, the product will not be oxidized even at a higher temperature between 450ºC and 500ºC(dependant on grade). |
| High heat-shock resistance | Coefficient of thernal expansion is very low as compared with that of other metal materials. The product withstands a repetition of abrupt temperature change, incurring little crack. It should also be noted that the product impregnated with resin or metal has a somehow lower heat heat-shock resistance. |
| Self-lubricating property | The product represents an outstanding self-lubrication, namely, it can be used without lubrication. Owing to this important nature, the product is very suitable for use where undersirable contamination by lubricant or similar accuracy to the case of ordinary metal materials. |
| Excellent machinability | The product has an excellent machinability, and can be machined on machine tools such as lathes, drilling machines, milling machines, etc., obtaining the similar accuracy to the case of ordinary metal materials. |
| Others | One of the major advantages of carbons is its porosity. By ipregnating the carbons with a resin or the like in the pores, they can be made impervious. After such treatment, carbons may be used as sealing materials. Further with this treatment, mechanical strength such as compressive strength, bending strength, etc. of carbons can be increased also along with its improved wear resistance. It should be noted that consultation should be made with us for examination of your intended uses of the product under any applicable regulations. |
Bearings

- Chemical pump bearings
- Water pump bearings
- Various pump bearings (for nuclear power plant, vessels, etc.)
Blades

- Automotive vacuum pumps
- Industrial vacuum pumps
- Industrial blowers
Packings

- Compressors
- Generators
Seal rings

- Mechanical seal rings (chemical pumps, refrigerators)
Characteristics
| Grade | Composition | Specific density |
Hardness (Shore) |
Bending strength (MPa) |
Compressive strength (MPa) |
Modulus of elasticity (GPa) |
Coefficient of thermal expsnsion (X106/ºC) |
Thermal conductivity (W/(m・ºC)) |
Maximum operating temp.(ºC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCB-1 | Graphite carbon |
1.70 | 58 | 48 | 108 | 4 | 35 | 350 | |
| HCB-1T | Graphite carbon |
1.74 | 66 | 57 | 137 | 13.7 | 4 | 35 | 350 |
| HCB-1F | Resin impregnated |
1.82 | 76 | 62 | 166 | 13.7 | 5 | 35 | 170 |
| HCB-3 | Graphite carbon |
1.68 | 55 | 42 | 98 | 11.7 | 4 | 32 | 350 |
| HCB-3F | Resin impregnated |
1.82 | 76 | 59 | 176 | 15.7 | 7 | 32 | 170 |
| HCB-30 | Graphite carbon |
1.67 | 55 | 39 | 98 | 11.7 | 4 | 41 | 350 |
| HCB-30T | Graphite carbon |
1.75 | 68 | 53 | 135 | 13.5 | 4 | 41 | 350 |
| HCB-5 | Electro graphite |
1.74 | 50 | 39 | 98 | 7.8 | 3 | 164 | 400 |
| HCB-7 | Graphite carbon |
1.75 | 67 | 42 | 137 | 12.7 | 3 | 39 | 350 |
| HCB-7F | Resin impregnated |
1.86 | 90 | 60 | 215 | 15.7 | 7 | 39 | 170 |
| HCB-8 | Graphite carbon |
1.62 | 79 | 48 | 176 | 11.7 | 4 | 12 | 350 |
| HCB-8F | Resin impregnated |
1.72 | 100 | 61 | 255 | 13.7 | 7 | 12 | 170 |
| HCB-85D | Resin impregnated |
1.70 | 100 | 69 | 255 | 14.7 | 8 | 12 | 200 |
| HCB-10 | Graphite carbon |
1.66 | 57 | 42 | 98 | 11.7 | 4 | 35 | 350 |
| HCB-10F | Resin impregnated |
1.80 | 75 | 59 | 147 | 13.7 | 5 | 35 | 170 |
Applications
Static pressure air bearings
A carbon material for static-pressure air bearings with this porosity — characteristic of carbon — being controlled in a special process.
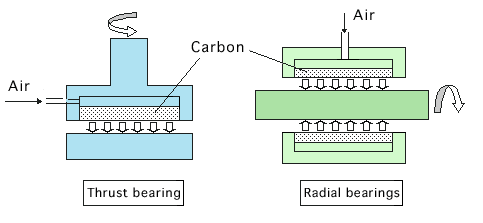
The shaft and bearing made contactless by air pressure improves wear and rolling friction loss considerably. The product best recommends itself in high-speed, high-precision rotating equipment.
Inquirer about product
Please subscribe our technology eNewsletter!
Inquiry about product
Please inquire about product, technology or samples from here.