June 19 2025
Resonac Corporation (President and CEO: Hidehito Takahashi, hereinafter “Resonac”) is set to begin evaluation experiments aboard the International Space Station on molding compounds for semiconductors designed to reduce the incidence of soft errors caused by cosmic rays.*1
The experiment has been commissioned to the U.S. commercial space company Axiom Space,*2and in April 2025, Resonac, delivered an operational evaluation device equipped with evaluation semiconductor chips to Axiom Space to be launched to the space station on a resupply mission this fall. Confirmation of the material’s effectiveness in reducing soft errors is expected to contribute to the improvement of existing space-oriented semiconductor performance and facilitate the application of ground-based semiconductors for space use.
Over the last decade, satellite launches have increased approximately elevenfold,*3 with further growth anticipated. Artificial satellites are equipped with semiconductors (processors) to process large amounts of data for purposes such as Earth observation and communications. However, processors designed for space applications tend to prioritize stability, resulting in lower computational capabilities compared to processors used on the ground.
On the other hand, there is a growing demand for improved computational capabilities in processors, driven by trends such as enabling satellites to make autonomous decisions—like the small lunar landing demonstrator “SLIM,” which independently explored its landing site through image processing—and efforts to minimize communication delays by linking low Earth orbit satellites, as seen with projects like “Starlink,” as well as integrating data center functions onboard satellites.
In this context, one of the challenges in enhancing computational capabilities for space processors is addressing soft errors caused by cosmic rays.
To address this issue, Resonac has developed prototype molding compounds for semiconductors blended with a compound that absorbs neutrons,*4 which are present in cosmic rays and cause soft errors. *5 In ground-based evaluation experiments, this material successfully reduced the soft error rate by approximately 20% in the simplest circuit (flip-flop circuits). To further advance these experiments, Resonac decided to transport semiconductor chips utilizing this molding compounds to the space station, where the chips will be operated both inside the station and outside the station on the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) platform to evaluate the soft error mitigation effects in real-world conditions. Resonac has entrusted the launch and experimental support to Axiom Space. By analyzing the impact of the radiation spectrum in space—which cannot be replicated in ground-based tests—Resonac aims to identify the characteristics required for semiconductor materials designed for space applications and obtain critical data for the development of high-performance semiconductor materials.
If this experiment confirms the material’s ability to reduce soft errors, nearly identical ground-based semiconductor chips could potentially be adapted for space use without significant alterations. This would enable cost reductions in manufacturing space-oriented semiconductors as well as functional enhancements. While there are alternative methods to mitigate soft errors, achieving this effect through molding compounds offers a simpler approach and may contribute to significant cost savings in peripheral design.
Aiming to achieve its Purpose, “Change society through the power of chemistry,” Resonac established a community named “REBLUC (Resonac Blue Creators)” in 2022, where employees voluntarily take initiative in activities. This experiment is promoted by members of REBLUC who desire to contribute to society through the development of cosmic materials.
Resonac aims to expand its development into semiconductor materials for satellites, space data centers, lunar bases, and lunar rovers in the future.

Operational evaluation device equipped with semiconductor chips for evaluation
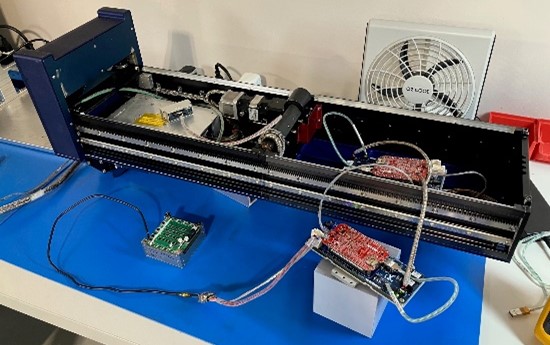
Space environment exposure experiment device equipped with an operational evaluation device

Molding compounds
- *1High-energy radiation found in space, including particle radiation like alpha rays, beta rays, neutron rays, and proton rays, as well as high-energy electromagnetic radiation like gamma rays and X-rays.
- *2Axiom Space is a Houston-based company building the world’s first commercial space, providing end-to-end human spaceflight services, and developing next-generation spacesuits for the Moon and low-Earth orbit.
- *3Cabinet Office, Government of Japan’s Space Development Strategy Promotion Bureau: Reference document “Current Environment and Future Outlook of Space Transport,” Material 2 (Japanese)
- *4Neutral particles within atomic nuclei, known to trigger soft errors upon collisions with semiconductor circuits in electronic devices.
- *5Patent application numbers:特願2025-051405、特願2025-051331